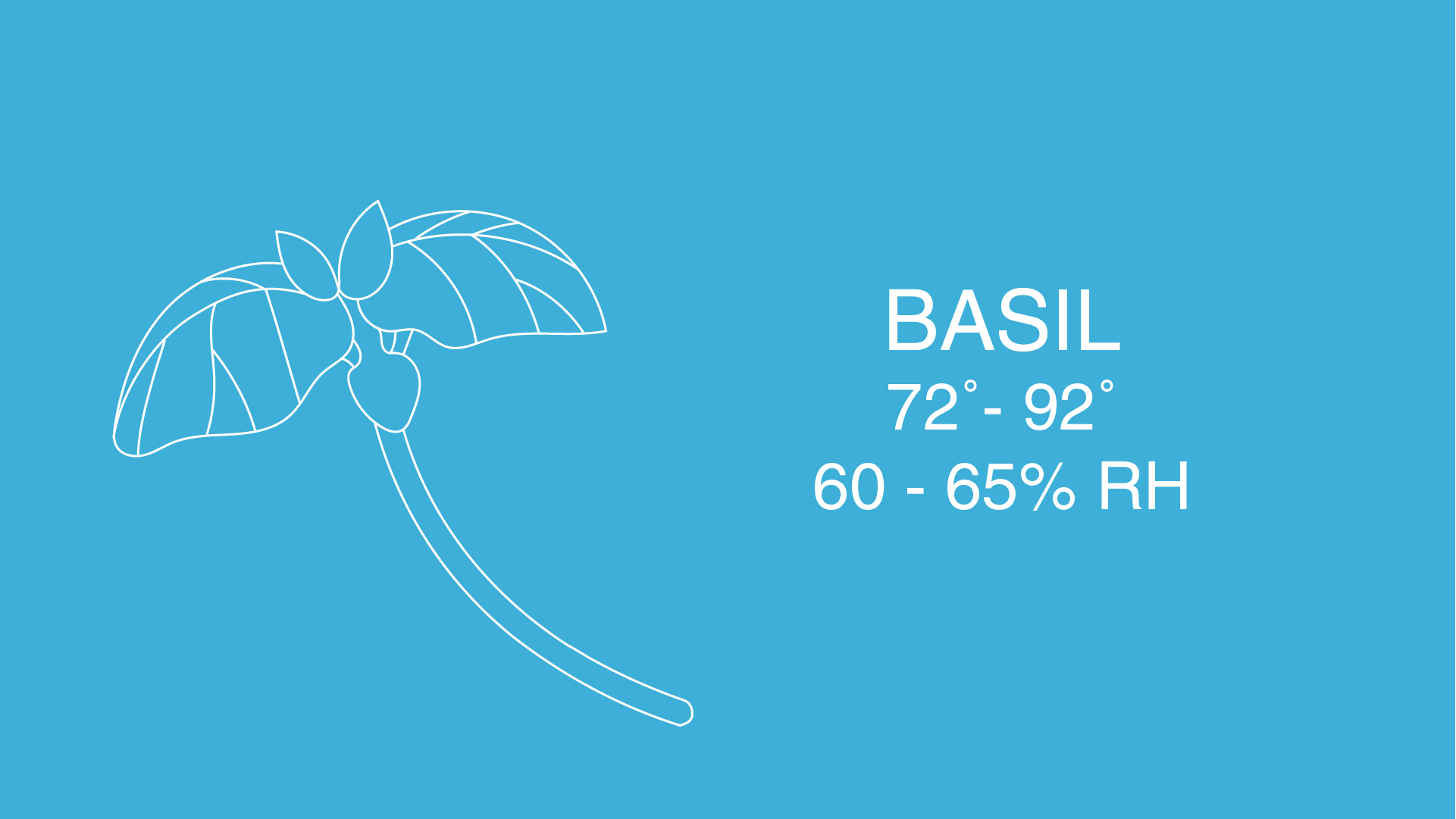
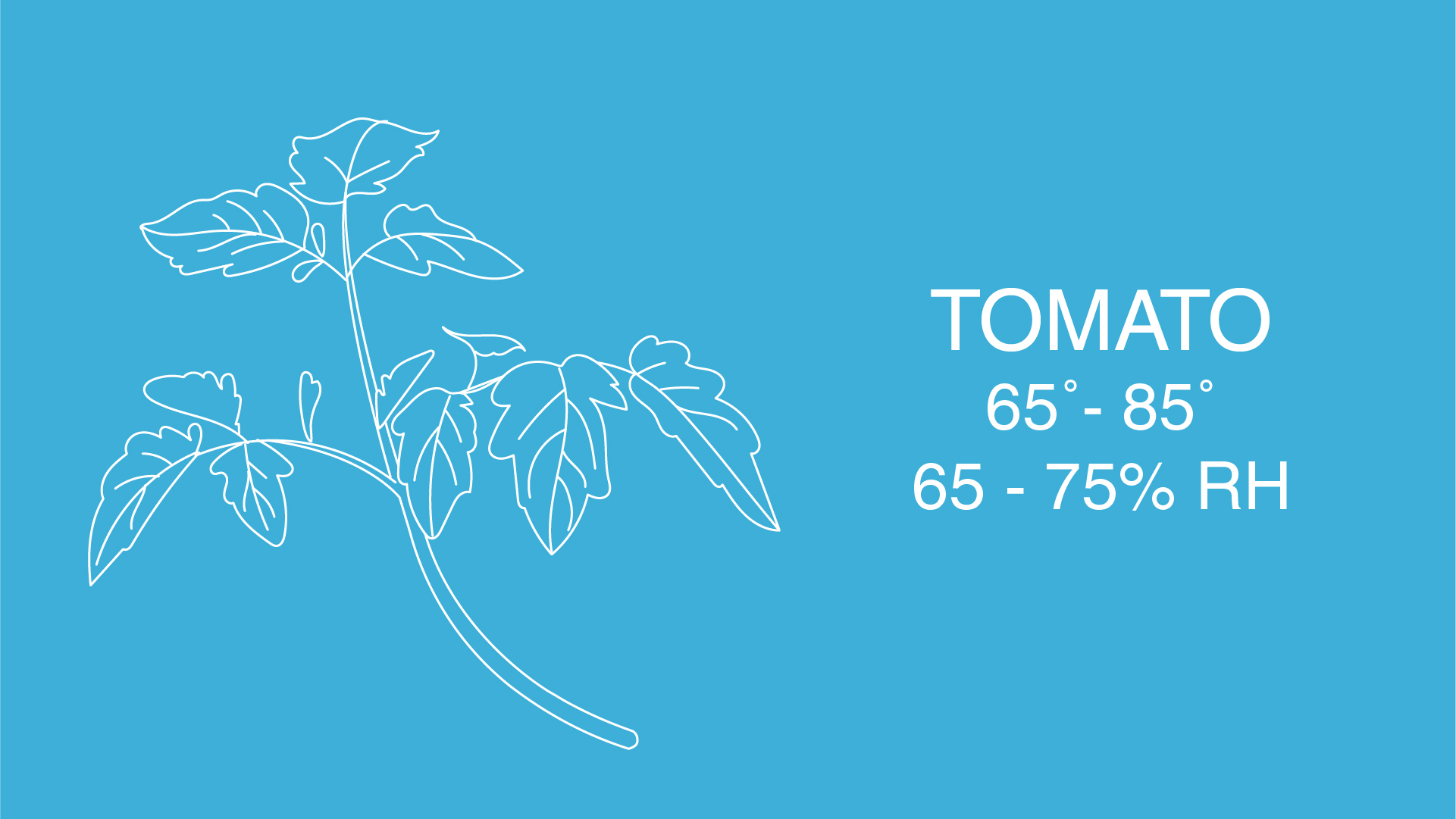
Plants rely heavily on their environment for growth and self-maintenance, taking in sunlight for photosynthesis and using the air to stay cool and as a source of CO2. Different plants prefer different conditions so it’s important that their ambient temperature and humidity are just right. But because these two factors drastically vary during seasonal shifts, the plant’s growth can be limited.
If plants are grown inside, they greatly benefit from controlled temperature and humidity since they won’t have to deal with extreme changes. They can enjoy their ideal weather conditions on a constant basis which will accelerate their growth and improve their yield. Temperature and humidity are controlled indoors using a ventilation system that expels stale air while replacing it with fresh air. This also prevents hot or humid patches by matching the grow tent’s conditions with that of the outside. Other benefits of growing indoors include stronger stems and preventing mold and pests from gathering.
Whether you are starting out with a grow tent or running a small operation with a grow room, an inline duct fan is the most vital tool you have to ventilate your grow space and controlling its temperature and humidity. Beyond that, your indoor growing climate conditions may still vary. So here, we are going to see how each factor impacts your grow success and how to manipulate them.
What is Temperature?
Temperature is one of the four primary environmental control factors that you as a grower will need to track and adjust to maximize yields. The other factors are humidity, lighting, and ventilation. Temperature is important to perfect because it affects how well seeds germinate and how efficient plants can photosynthesize, flower, and fruit. Ideal grow room temperatures vary based on what you want to grow but most plants thrive at room temperature.
For plants to reach their full potential, they must be able to grow specific temperature ranges. Otherwise, their yields may be smaller, of lower quality, or won’t survive. One of your many challenges will be maintaining your plant’s ideal temperature and keeping your grow space cool. Heat sources like your grow light and the outdoor climate, depending on your situation, can increase your grow space’s temperature.
If the grow tent temperature is too high your plants will shut its stomata, which is used to transpire water vapor. The water trapped may overheat and result in poor growth and unhealthy plants. Moreover, the sugar energy your plants worked to use on making flowers and fruit would instead be used to sustain itself.
While you want to keep temperatures low, you also don’t want them too low since cold also causes damage to your plants. Besides generally slowing down and minimizing growth, coldness will freeze your plants’ cells and cause tissue death if temperatures are too low.
What is Relative Humidity?
Relative Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air at a given temperature, invisible to the naked eye as a gaseous state. There are many sources of water vapor in the atmosphere including animals breathing, evaporation from snow and bodies of water, and plants transpiring. Eventually, the water vapor condenses and becomes visible as clouds or fog.
Plant growth is influenced by relative humidity because it affects how much water your plants move through their stem and leaves.
The more humidity that’s in the air, the less moisture it can “hold” since the air can only support so much water vapor. Plants transpire much like we humans sweat which adds to the relative humidity. This is done by opening their stomata, which is the only time plants can photosynthesize. If the stomata close, photosynthesis stops completely.
 Make sure to properly seal and insulate your room to lessen the outside factors' effect on your grow tent ventilation.
Make sure to properly seal and insulate your room to lessen the outside factors' effect on your grow tent ventilation.About 5% of the water plants take in is retained, with the other 95% transpired back into the environment. With this much water returning to the air, it’s important to keep your grow tent’s relative humidity stable and at the right level. Doing so will give your plants space to transpire, allowing it to stay cool and take in nutrients from its soil.
If your grow room’s humidity is too high, your plants will not be able to transpire and will retain the water it absorbed. This subjects them to overheating and drying up, while at the same time not taking in more water and nutrients. High humidity also invites bud rot and mold and mildew build-up. Conversely, if your grow room’s humidity is too low your plants will dry up since they will try to transpire to compensate. Your plants will then close their stomata to prevent itself from drying up further, stopping their photosynthesis.
Thermometers and Hygrometers for Grow Tents
Monitoring your grow tent’s temperature and humidity is vital in controlling their levels, especially because different plants have different climate preferences. Whether standalone or built into existing grow technology, you will need to use thermometers and hygrometers to track current levels. These measuring devices will display your grow tent’s current temperature and humidity respectively and enable you to grasp grow space climate control.
Now that you know what your plant’s ideal conditions are, how do you stabilize them when spikes and dips occur? Temperature and humidity cycles should ideally appear as a smooth moving wave, as opposed to jagged spikes and valleys in your graphical readings. There are several signs that you can look out for using your digital thermometer and hygrometer including the impact of the time of day, indoor light cycle, and water cycle. Extreme highs or lows in your readings are an obvious sign to balance the climate conditions.
 Measuring tools like thermometers and hygrometers will help you get a clear picture of your grow tent's climate conditions, allowing you to take appropriate action when needed.
Measuring tools like thermometers and hygrometers will help you get a clear picture of your grow tent's climate conditions, allowing you to take appropriate action when needed.How to Adjust Temperature & Humidity
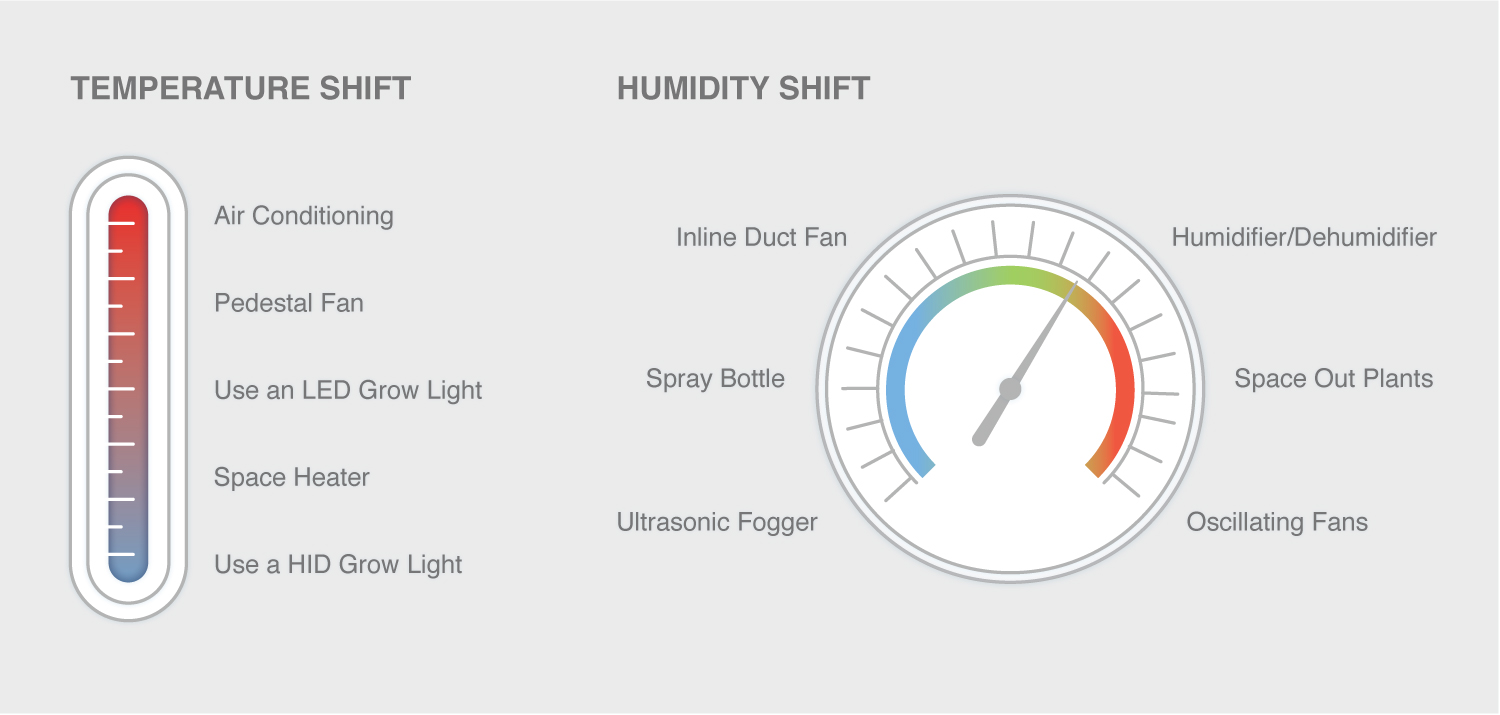
The diagram below lists a sample of methods and their use scenarios when conditions get too hot or humid and vice versa. Before using any of these tools, you can diminish the outdoor climate’s effect and avoid fluctuations and light leaks by properly sealing and insulating your grow space. Be sure to space out your plants as well, since overcrowding them will increase humidity levels. If you need to make adjustments to fit your needs, use these and other tools to help you stabilize your grow environment: